STAGE 1: REQUIREMENTS DEFINITION
The first stage comprises defining the basis for Technology Qualification, namely what the
technology is, how
it functions, how it is used, how it is expected to perform and what the overall aims/targets of the
qualification process are. This stage can be regarded as defining the inputs to the qualification plan and
process because all qualification activities refer back to the requirements defined at this stage.
REQUIREMENT CATEGORIES
A list of potential aspects which may be considered in this stage are listed below.
Technology Description
Definition of the general design
concept/description and technology intent.
Current stage of development/qualification.
Current stage of development/qualification and
pre-existing qualification
evidence/certification,
including the technical risk register (TRR) and
research
and development (R&D) methodologies used.
Functions and functional limitations.
Functions and functional limitations, including
processes, modes of operation and use cases
for all life cycle stages, such as installation
and
decommissioning requirements as well as
reliability,
availability and maintainability (and safety);
RAM(S) targets, i.e., design life.
Similarities/differences with other technologies.
Technology boundaries.
Technology boundaries and boundary design
conditions
(i.e., critical parameters) as well as the
interface(s)
with other parts of the sub-system/system and
environmental operating conditions (e.g., limit
states).
Relevant literature.
Relevant class rules/legislation/standards/industry
practices can be found here.
For technologies which have been incrementally
modified
to meet more stringent requirements,
qualification
activities may be encapsulated by industry
standards.
Material properties, manufacturing as well as
quality
assurance and quality control (QA/QC) aspects.
Relevant areas of expertise required for further
development (and qualification).
Performance Requirements
Acceptance criteria.
A common set of acceptance criteria against which
all activities are assessed in terms of:
Safety,
functionality, reliability, availability,
environmental
impact, maintainability and performance goals.
Identification of critical parameters. Much of
this
should come from e.g. Basis of Design or other
system engineering tools.
Health, Safety and Environment (HSE) targets or
constraints.
Adopted standards of reference.
Market needs.
Human system integration.
Scope of Qualification
Formation of Qualification Team.
Formation of the Qualification Team and partner
obligations. Definition of respective roles.
The
Qualification Team typically comprises the
vendor/supplier/developer plus reviewers and
may involve other stakeholders (e.g.,
regulatory
agencies, operators and end-users). Conflicts
of
interest need to be identified in order to
ensure
the objectivity of Team members.
Goals and requirements of all relevant
stakeholders (e.g., target TRL).
Confidentiality aspects with respect to
background intellectual property.
Identification of decision gates and/or milestones.
Resources required to carry out the TQ programme.
Project management.
Project management including project timeline,
milestones, budget, description of
deliverables,
communication strategy, data management and
system
security. Contingencies are likely to feature
in the
project timeline and budget to allow for
unforeseen
circumstances (i.e., premature failure of a
component
which then must be remanufactured and
retested).
Requirements Definition Example: Generic Mooring Connector
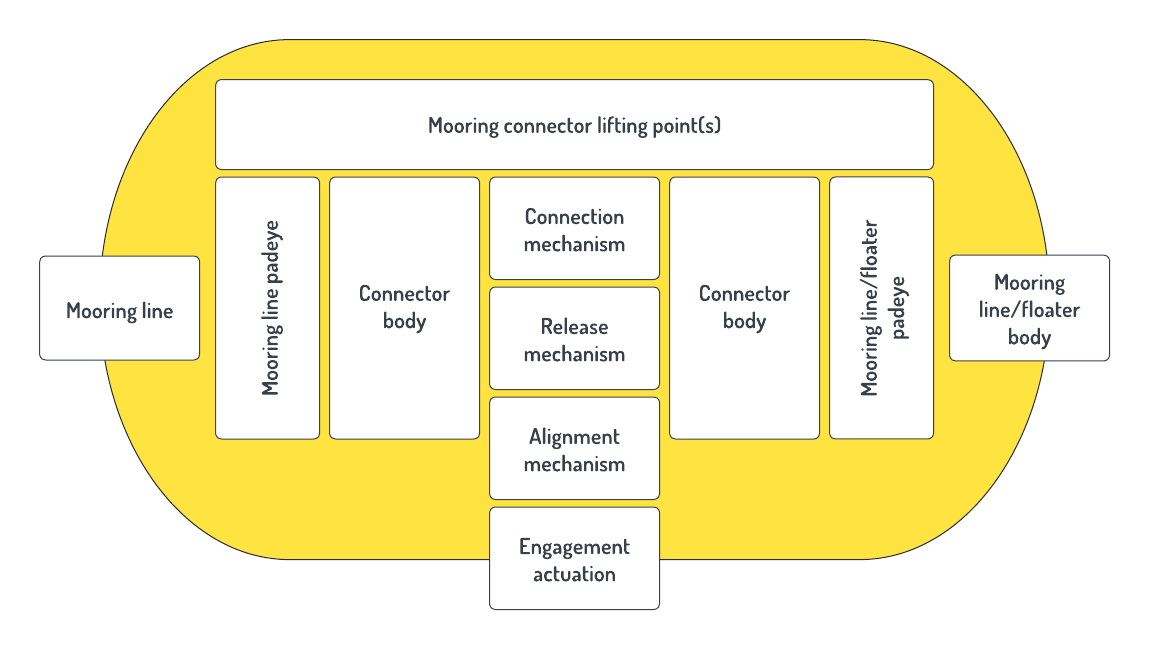
To provide an example of this stage, a
generic mooring connector with quick-release capabilities (pictured on the left) is
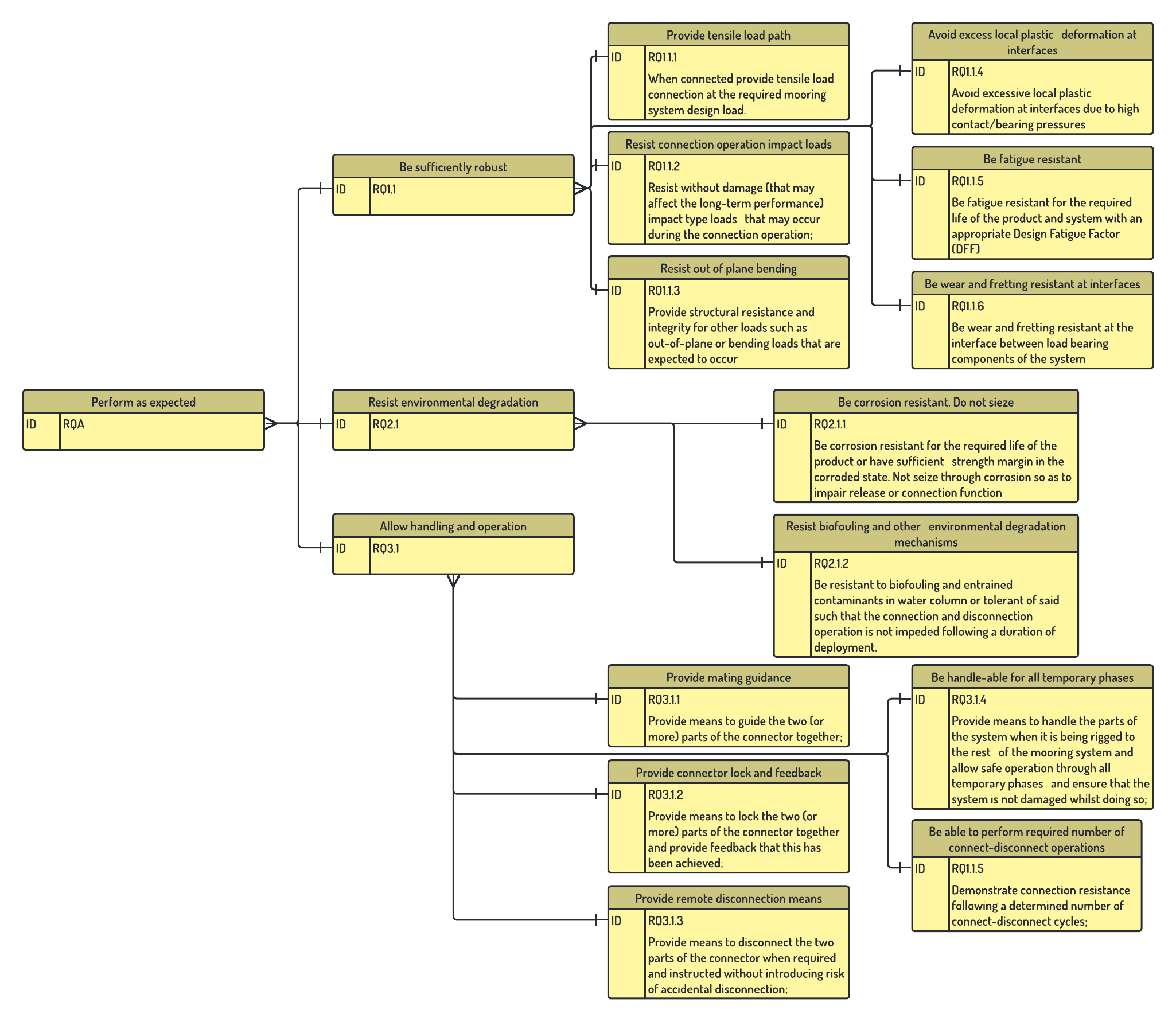
considered. Performance requirements are
shown in the diagram below. It can be seen that there is one overall system requirement
RQA which is proceeded by several Level 1 requirements; RQ1.1 ,
RQ2.1 and RQ3.1 , for example Allow handling and
operation . Each of these is made up of Level 2 requirement categories which can
be used to define TQ activity targets.